
While the former is a container specifically designed to isolate mobile devices from network communications and, at the same time, help with the safe transportation of evidence to the laboratory, the latter, is a power source embedded inside the Faraday box/bag. Phone jammerĬredit: Got myself a Cell Phone Jammer by Baishampayan Ghose / (CC BY-ND 2.0)Ī Faraday box/bag and external power supply are common types of equipment for conducting mobile forensics. Mobile devices are often seized switched on and since the purpose of their confiscation is to preserve evidence, the best way to transport them is to attempt to keep them turned on to avoid a shutdown, which would inevitably alter files. Network isolation is always advisable, and it could be achieved either through 1) Airplane Mode + Disabling Wi-Fi and Hotspots, or 2) Cloning the device SIM card. There are two major risks concerning this phase of the mobile forensic process: Lock activation (by user/suspect/inadvertent third party) and Network / Cellular connection. Some legal considerations go hand in hand with the confiscation of mobile devices. What are the steps in the mobile forensics process? 2.1 SeizureĬredit: mobile phone evidence box by jon crel / (CC BY-ND 2.0)ĭigital forensics operates on the principle that evidence should always be adequately preserved, processed, and admissible in a court of law. During the inquiry into a given crime involving mobile technology, the individuals in charge of the mobile forensic process need to acquire every piece of information that may help them later – for instance, device’s passwords, pattern locks or PIN codes. Following correct methodology and guidelines is a vital precondition for the examination of mobile devices to yield good results.Īmong the figures most likely to be entrusted with the performance of the following tasks are Forensic Examiners, Incident Responders, and Corporate Investigators. Nevertheless, one should know that the mobile forensics process has its own particularities that need to be considered.

Usually, the mobile forensics process is similar to the ones in other branches of digital forensics. To achieve that, the mobile forensic process needs to set out precise rules that will seize, isolate, transport, store for analysis and proof digital evidence safely originating from mobile devices. The mobile forensics process aims to recover digital evidence or relevant data from a mobile device in a way that will preserve the evidence in a forensically sound condition. Did you know that 33,500 reams of paper are the equivalent of 64 gigabytes if printed? Storage capacity of 64 GB is common for today’s smartphones.
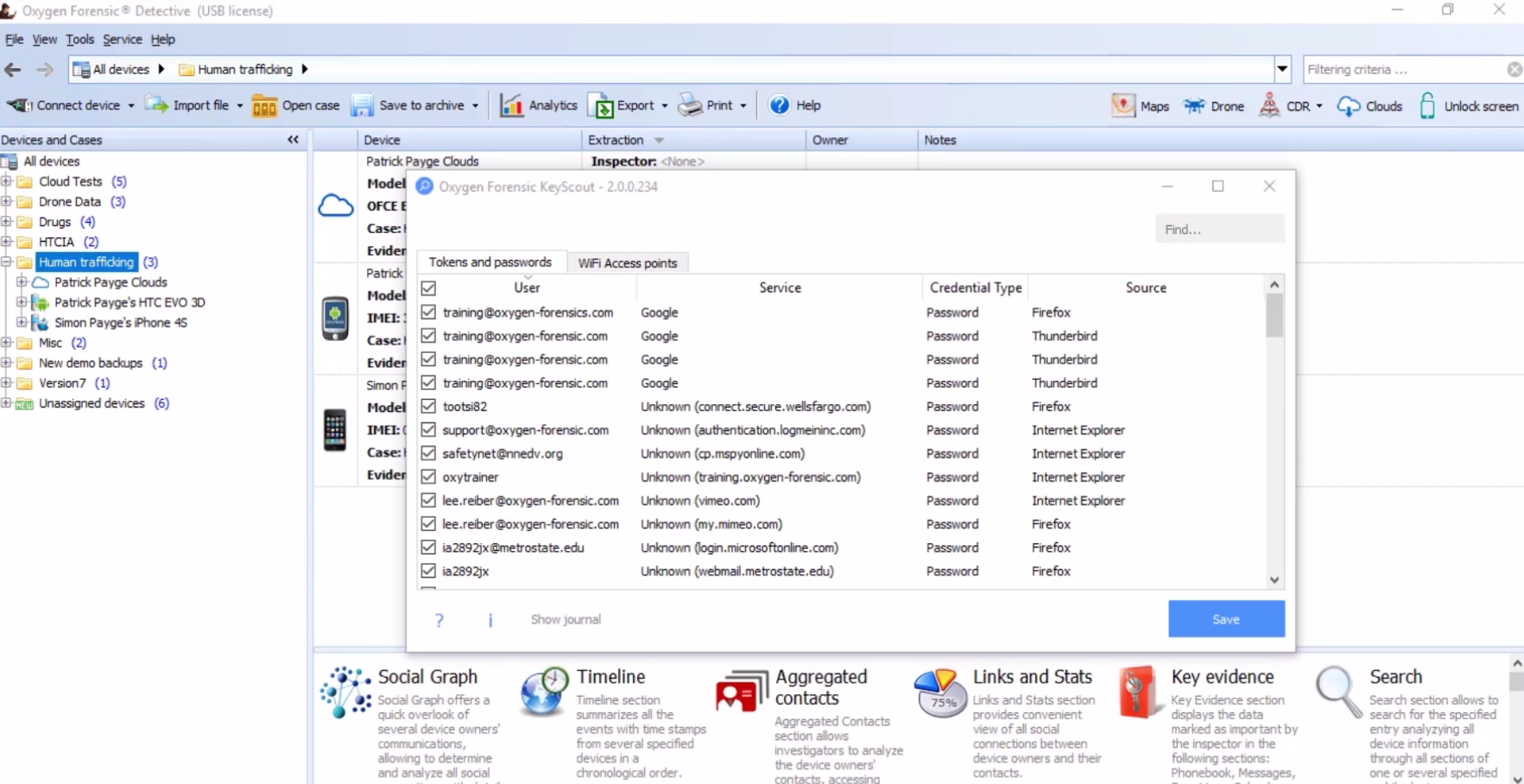
#G OXYGEN FORENSICS PROFESSIONAL#
As the mobile devices increasingly continue to gravitate between professional and personal use, the streams of data pouring into them will continue to grow exponentially as well. Most people do not realize how complicated the mobile forensics process can be in reality. One good display of the real-life effectiveness of mobile forensics is the mobile device call logs, and GPS data that facilitated solving the 2010 attempted bombing case in Times Square, NY.Ĭrimes do not happen in isolation from technological tendencies therefore, mobile device forensics has become a significant part of digital forensics.


Information that resides on mobile devices (a non-exhaustive list): Being something like a digital extension of ourselves, these machines allow digital forensic investigators to glean a lot of information. Nowadays, mobile device use is as pervasive as it is helpful, especially in the context of digital forensics, because these small-sized machines amass huge quantities of data on a daily basis, which can be extracted to facilitate the investigation. In 2015, 377.9 million wireless subscriber connections of smartphones, tablets, and feature phones occurred in the United States. The proliferation of mobile technology is perhaps the main reason, or at least one of the main reasons, for these trends to occur in the first place. Mobile devices are right in the middle of three booming technological trends: Internet of Things, Cloud Computing, and Big Data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
